Q2 Commercial Insurance Rates Reverse Seven-Year Climb as Global Competition Intensifies
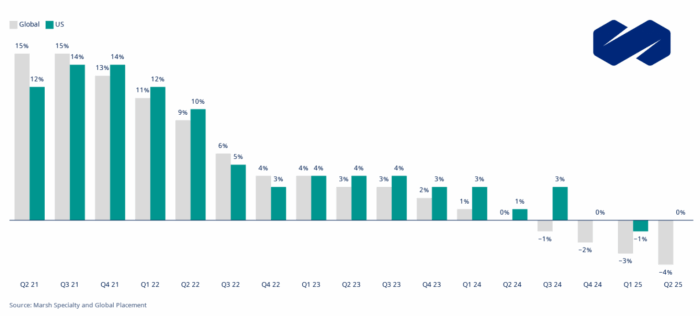
Global commercial insurance rates declined 4% in the second quarter of 2025, marking the fourth consecutive quarterly decrease and ending seven years of quarterly rate increases, according to the Marsh Global Insurance Market Index.
The global rate environment reflects a dramatic reversal from the hard market conditions that dominated the insurance landscape for nearly a decade. While most regions experienced significant declines — with the UK dropping 6% and the Pacific region falling 11% — the U.S. market remained flat in Q2, suggesting more complex underlying dynamics, according to Marsh.
U.S. property insurance led the decline domestically, dropping 9% for the second consecutive quarter as insurers competed aggressively for business and benefited from decreasing reinsurance costs. This contrasted sharply with casualty lines, which surged 9% nationally, driven primarily by persistent challenges in auto liability and umbrella coverage, the report said.
Casualty rate increases proved particularly pronounced when excluding workers’ compensation, jumping 12%. Auto liability rates continued climbing due to large jury verdicts and escalating repair costs, while umbrella and excess liability markets saw risk-adjusted rates rise 18% — up from 16% in the prior quarter, the report said. Some insurers now cap capacity at $10 million per risk due to adverse litigation developments, Marsh noted.
Cyber insurance rates bucked global trends with a more modest 3% decrease in the U.S., representing the ninth-consecutive quarter of reductions. However, organizations showed less appetite for higher limits compared to previous periods, and cyber insurers grew increasingly concerned about coverage restrictions for third-party privacy claims and war exclusion wording amid ongoing global tensions.
Competition Creates New Opportunities and Risks
The shifting rate environment has fundamentally altered the relationship between insurers and clients, Marsh said. In property lines, increased capacity fostered competition across industries previously considered challenging, including multi-family housing, warehousing, and food and beverage sectors, according to the report. Clients typically achieved coverage enhancements such as higher limits, revised definitions, and lower deductibles.
However, casualty markets present a different picture. Umbrella insurers shifted away from single tower capacity toward supported umbrella options due to severe claims frequency. Four London market closures in 2024 reduced available capacity, while some high-excess insurers raised minimum prices to $10,000 per million. Lead umbrella programs with favorable loss experience still faced rate increases of 12% to 15%, while those with adverse development saw increases exceeding 30%, Marsh said.
In financial and professional lines, which remained flat after 11 consecutive quarters of declines, insurers increasingly sought minimum premium levels higher than current pricing, with some opting out of renewals or reducing capacity entirely.
“Despite the softening global market, clients also explored alternative risk financing strategies, such as self-insurance, parametric coverage, and captive insurance options,” said John Donnelly, president, global placement for Marsh. “In addition to the continued formation of new captives, more companies are optimizing existing ones as part of their long-term risk finance strategy.”
Market Vulnerabilities Remain Despite Rate Relief
Despite the rate relief, underlying market vulnerabilities suggest the current environment could shift rapidly. Property markets remain susceptible to natural disasters, which could quickly reverse favorable pricing trends. “A significant natural disaster could rapidly alter the environment,” the report said.
Casualty markets face structural challenges beyond rate adjustments. Rising reserves and medical costs in workers’ compensation may impact future rates, while general and product liability claims showed greater severity, particularly related to pandemic-era incidents. Casualty insurers expanded coverage restrictions to include PFAS, biometrics, and cyber exposures, with additional exclusions for real estate and hospitality sectors covering sexual abuse and human trafficking claims, the report said.
The cyber market, while experiencing rate decreases in the quarter, continues to face evolving threats including increased activity from sophisticated hacking groups like Scattered Spider, which targeted major companies across retail, insurance, financial, and airline sectors in the second quarter. Third-party privacy claims also increased due to allegations of wrongful data collection and sharing, prompting some insurers to clarify and restrict coverage for these exposures, the report said.
View the global report here. &